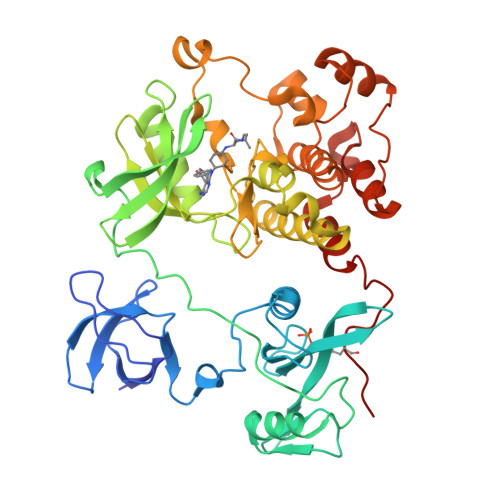
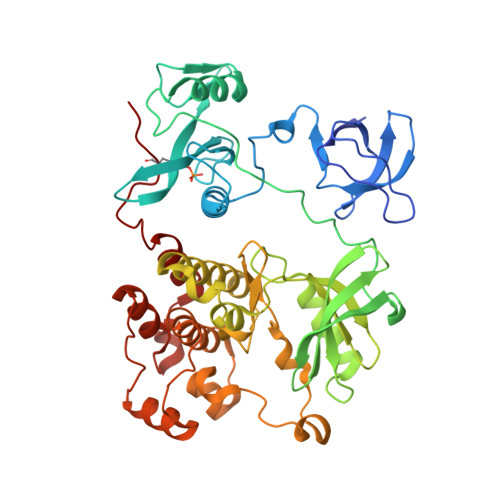
Activity cliff for 7-substituted pyrrolo-pyrimidine inhibitors of HCK explained in terms of predicted basicity of the amine nitrogen.
Yuki, H., Kikuzato, K., Koda, Y., Mikuni, J., Tomabechi, Y., Kukimoto-Niino, M., Tanaka, A., Shirai, F., Shirouzu, M., Koyama, H., Honma, T.(2017) Bioorg Med Chem 25: 4259-4264
- PubMed: 28662963
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bmc.2017.05.053
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
5H09, 5H0B, 5H0E, 5H0G, 5H0H - PubMed Abstract:
We previously reported the structure-based design of a highly potent hematopoietic cell kinase (HCK) inhibitor, a pyrrolo-pyrimidine compound designated RK-20449, for treatment of recurrent leukemia. Herein we report the synthesis and structure-activity relationships of some amino acid derivatives of 7-substituted pyrrolo-pyrimidine. Although these derivatives had the same predicted binding conformation as RK-20449, their IC 50 values were 100-1000 times larger than that of the parent compound. We assumed that the basicity of the amine nitrogen, which formed an ionic bond with Asp348 of HCK, markedly affected inhibitory activity against HCK. The pKa values of the nitrogen were predicted by means of an ab initio quantum mechanical method, and complexes of the derivatives with HCK were analyzed by X-ray crystallography. We observed a significant correlation between the predicted pKa and IC 50 values, and the crystal structures of the less potent derivatives showed various types of defects around the ionic bond.
Organizational Affiliation:
Drug Discovery Computational Chemistry Platform Unit, RIKEN Center for Life Science Technologies, 1-7-22 Suehiro-cho, Tsurumi-ku, Yokohama, Kanagawa 230-0045, Japan.